How to configure SAMBA
SAMBA is a Windows AD and SMB/CIFS fileserver for UNIX. To use this service you need to edit its configuration file /etc/samba/smb.conf. Structure of this file is similar to windows ini-files:
[section] name = value
So, let's edit our configuration file, open it in your favorite text editor and let's go.
Write here your workgroup, this group will be visible to your windows clients:
[global] # Change this to the workgroup/NT-domain name your Samba server will part of workgroup = WORKGROUP
Don't forget to specify networks that can use the server:
[global]
hosts allow = 192.168.0.128/28 192.168.1.0/24
Now let's specify some share for our windows friends:
[tmp] comment = Temporary data path = /var/tmp browseable = yes writable = yes public = yes
Here section name is the name of shared resource (what clients see); comment is a description of the share; path is the full path to the shared directory on your samba server. All other options (and more) are described in the samba documentation.
Check rights for directory in "path = shared_directory_path"
It's time to start the service.
root@dilos:~# svcs smbd STATE STIME FMRI disabled 14:54:55 svc:/smbd:default root@dilos:~# svcadm enable smbd root@dilos:~# svcs smbd STATE STIME FMRI online 17:15:15 svc:/smbd:default
Let's check the server is working now:
debian# smbclient -L 192.168.13.3
Enter root's password:
Domain=[DILOS] OS=[Windows 6.1] Server=[Samba 4.5.6-Debian]
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
print$ Disk Printer Drivers
tmp Disk Temporary data
IPC$ IPC IPC Service (Samba 4.5.6-Debian)
That's all. You can see in this output name of the shared resource (tmp) and its description (Temporary data).
Sometimes you may want to run windows name service, just start nmbd service like we did it with smbd:
root@dilos:~# svcs nmbd STATE STIME FMRI disabled 14:50:58 svc:/nmbd:default root@dilos:~# svcadm enable nmbd root@dilos:~# svcs nmbd STATE STIME FMRI online 17:27:10 svc:/nmbd:default
Another simple configuration:
[global] workgroup = DILOS server string = DilOS Example Server dns proxy = no interfaces = 172.16.1.0/24 log file = /var/log/samba/log.%m max log size = 1000 syslog = 0 panic action = /usr/share/samba/panic-action %d server role = standalone server passdb backend = tdbsam obey pam restrictions = yes unix password sync = yes passwd program = /usr/bin/passwd %u passwd chat = *Enter\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *Retype\snew\s*\spassword:* %n\n *password\supdated\ssuccessfully* . pam password change = yes map to guest = bad user usershare allow guests = yes [guest] comment = Example of shared resource path = /var/tmp/samba browseable = yes read only = no guest ok = yes
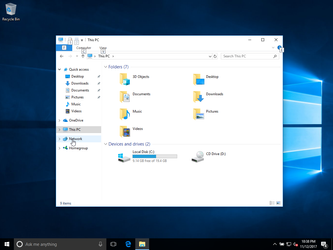
and the result on a windows computer, scan the network:
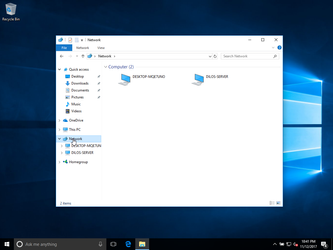
here we see the dilos server:
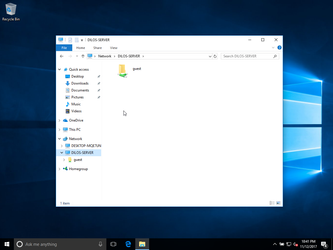
and the only shared resource from the configuration above (guest):
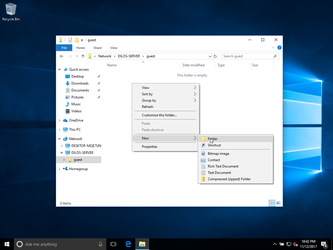
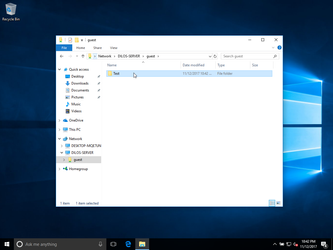
create a folder on the shared resource:
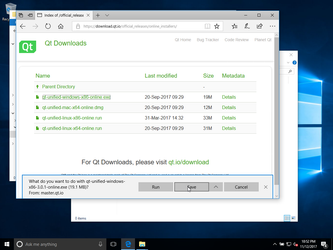
Now let's downlad something real from the Internet:
so, the file is local now:
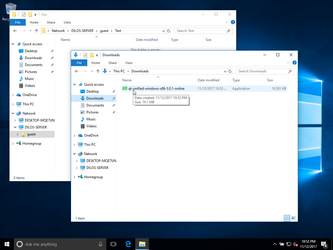
copy it to the shared resource:
See the properties of the file:
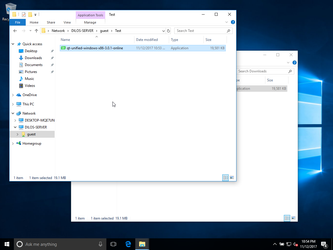
Now, let's copy it to the desktop:
et voilà: